Theme: Enlighten the Spectrum of Light
Opticsphotonics-2018
With the successful journey of Optics 2017 conferences in Las Vegas, USA, ConferenceSeries Ltd planned to continue its Optics conference series saga in Bucharest, Romania during November 22-23,2018. On behalf of the Organizing Committee of “9th World Congress on Optics, Photonics, and Telecommunication,” all the researchers, developers, and experts are warmly welcome from the field of Light and Communication to attend. Our aims are to unite all the people engaged in this enormous field and exchange the knowledge, discuss and look forward to the new way by interfacing new thoughts, also upgrading the limits of the future technology.
OpticsPhotonics2018 will create a platform to meet the renowned scientist, Innovators, industrialist and student of this field and explore the vast topic of Light by sharing and learning. The OpticsPhotonics2018 will be composed around the theme “Enlighten the Spectrum of Light”.
Optics is the science of light particularly, optics is a section of physics describing how light behaves and interacts with matter, involving the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use and detect the light.
Photonics is the technology of generating and harnessing light and other forms of radiant energy whose quantum unit is the photon, covering all light's technical applications over the whole spectrum; most photonic applications are in the scope of visible and near-infrared light.
Telecommunication is a vast range of transmission or exchange of signals/ information/ data by electronics means between themselves, it may be wired or wireless.
The OpticsPhotonics2018constitutes of Sessions like Keynote Speeches, Oral Presentations, Poster Presentations, Universal Workshops, B2B Meetings, Panel Discussions, Q&A sessions, Industry expert interactions. There are awards for some categories like Best Poster, Best Oral presentation, Young Researcher Forums (YRF), e-Poster presentations, Video presentations by the experts from both Industry & Academic.
OpticsPhotonics2018 unites specialists, leading researchers, scholars, scientists, educators from the different Engineering fields, and other related zones to connect and trade thoughts regarding the best in class advances identified with Optics, Photonics, and Telecommunication. The conference will also provide an insightful understanding of the issues arising out of the Light and the future concern and remedies from that. OpticsPhotonics2018 provides an Opportunity to interact with eminent Scientists, researchers, Business Leaders, experts from all over the world.
9th World Congress on Optics, Photonics and Telecommunication 2018 invite all interested participants to join us for this esteemed event at the exquisite destination Romania, Europe. For more information: conferenceseries.com
Why to Attend?
9th World Congress on Optics, Photonics, and Telecommunication, is among the World's leading technical Conference. The three-day event on optics, photonics, and telecommunication will host 60+ Scientific and technical sessions and sub-sessions on cutting-edge research and latest research innovations in the field of Light across the globe. Optics, Photonics, and Telecommunication 2018 will comprise of 18 major sessions designed to offer comprehensive sessions that address current topics in the various field of Light.
The attendees can find exclusive sessions and panel discussions on the latest innovations in Optics, Photonics, and Telecommunication by:
Target Audience
- Researchers
- Scientists
- Smart innovators
- Space science Engineers
- Mechanical Engineers
- Electrical engineers
- Computer science engineers
- Robotic technologist
- Design Engineers
- Gaming professionals
- Automation industry leaders
- Healthcare service providers
- Defense Research Professionals
- Automation industry leaders
- Managers & Business Intelligence Experts
- Advertising and Promotion Agency Executives
- Professionals in the media sector
- Professors
- Students
Conference Sponsor and Exhibitor Opportunities
The Conference offers the opportunity to become a conference sponsor or exhibitor.
Highlights of latest advances in Optics, Photonics and Telecommunications
Track 1: Optics
Optics is the outlet of physics that involves the properties of light and behavior, as well as its interactions with matter and additionally the development of instruments that use or understand it. it always describes the behaviour of ultraviolet, infrared and visual light. Because the light is an electromagnetic radiation like microwaves, radio waves exhibit similar properties and X-rays.
Optical phenomena may be accounted for exploitation classical electromagnetic rationalization of light. The entire electromagnetic descriptions of light are usually difficult to use in practice. Sensible optics is sometimes done using simplified models. Physical optics could be a additional comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects like optical phenomenon and interference that can't be accounted for in geometric optics. In general, geometric optics treats light as a group of rays that travel in straight lines and bend once they are going through or replicate from surfaces. Normally, the ray-based model of light was developed 1st, followed by the wave model of light. Progress in electromagnetic theory within the 19th century LED to the invention that light waves were actually radiation.
- Tissue optics
- Optical coherence tomography
- Biomedical Optics
- Optical instruments
- Visual effects
- Photography
- Telescope
- Optical microscopes
- Geometrical optics
- Optical lenses
- Optical computing Photonics for energy
- Photonic and optoelectronic materials and devices
- Communications and switching photonics
- Ultrafast electronics, photonics and optoelectronics
- Green Photonics
- Photodetectors, sensors and imaging
- Fiber optics devices
- Nonlinear optics and photonics
- Microwave photonics
- Optogenetics
- Optofluidics
Track 2: Optical Communication and Networks
Optical communications networks are enhancing an important role like there is high demand for capability links. DWDM which implies dense wavelength division multiplexing is widely deployed at the core networks to deliver high capability transport systems. Optical elements like tunable filters, termination devices, optical amplifiers transceivers, and add-drop multiplexers have become a lot of trustworthy and reasonable. Access network and metropolitan space networks are progressively built with optical technologies to beat the electronic blockage at network edges. Subsystems and new parts for terribly high-speed optical networks provide a brand-new design option. Free-space optical communication has been organized in space, whereas terrestrial forms are naturally restricted by weather, earth science and therefore the convenience of light Fibre optics communication.
- Optical signal communication
- Design management and optical networks
- Novel optical networks elements
- Optical fibre manufacturers and business analysis
- Advances in optical fibre communication
Track 3: Special issue on optoacoustic imaging and sensing
Optoacoustic or photoacoustic imaging involves the generation of ultrasound waves by transient light absorption. It is attractive from a biological perspective as it is insensitive to photon scattering within biological tissue and has non-invasive medical imaging capabilities. The power of the technique is that it draws upon the advantages of high optical absorption contrast and deep ultrasonic penetration to enable high-resolution optical visualization deep within tissue, giving it a potential edge over other high-resolution optical imaging modalities. It is also very versatile as a method and is the relatively low cost to implement. Thus, it has emerged as an important tool in biological and clinical applications.
The aim of this special issue is to provide an up-to-date picture of recent improvements in the capabilities of optoacoustic systems, such as through advances in technology, detection strategies and inversion techniques. It will also cover applications of the method across microscopy, tomography and sensing.
- Biomedical imaging
- Photoacoustic computed tomography
- General equation
- Universal reconstruction algorithm
- Simple system
- Biomedical applications
- Brain lesion detection
- Hemodynamics monitoring
- Breast cancer diagnosis
- Photoacoustic microscopy
Track 4: Semiconductor nanostructures for optoelectronics
Semiconductor nanostructures are part of an emergent class of materials that provide unprecedented levels of functionality in building devices for electronics and optoelectronics applications. Associated Nanoscale devices may be used to study new physics in low-dimensional systems and enable a route for the development of new technologies in key areas, such as communications and information processing, sensing and renewable energy as well as biomedicine.
This symposium was the fourth instalment of a highly successful biennial series that began in 2007. Bringing together researchers working in academia and industry, it presented the latest research in semiconductor Nanostructures and their applications to electronic, optoelectronic and photonic devices. Blending experimental with numerical and theoretical approaches, it covered all aspects of fundamental growth and material development, to interfaces, device integration and testing.
- Semiconductor nanostructures
- Locked laser diodes
- Optoelectronic Device Applications
- Quantum efficiency
- Semiconductor nanowires
- Optoelectronics and photonic applications
Track 5: Quantum optics
A quantum detector could be a device that exploits quantum correlations, like a quantum trap, to attain a sensitivity or resolution that's higher than will be achieved exploitation only classical systems. A quantum device will measure the impact of the quantum state of another system on itself. The mere act of measure influences the quantum state and alters the likelihood and uncertainty related to its state throughout measuring. The Defense, Advanced analysis comes Agency has recently launched a search program in optical quantum sensors that seeks to use concepts from quantum science and quantum imaging, like quantum lithography and also the noon state, so as to attain these goals with optical sensing element systems like measuring system. Quantum detector is additionally a term utilized in different settings wherever entangled quantum systems are exploited to form higher atomic clocks or a lot of sensitive magnetometers. The marketplace for a quantum dots primarily based product, such as new tv screens, is projected to achieve $3.5 billion by 2020. The bulk of this growth can return from enlarged demand in the United States.
- Quantum Photonics
- Quantum Dots
- Quantum Lasers
- Quantum Optoelectronics
- Dipolar Quantum Gases and Liquids
- Quantum Indeterminacy
Track 6: Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy and spectrography are for the measurement of radiation intensity as a function of wavelength and used to describe experimental spectroscopic methods. Spectral measurement devices are referred to as spectrometers, spectrophotometers, spectrographs or spectral analyzers.
Spectroscopy is the study of materials interaction with light, generally through absorption, scattering or transmission and is a very powerful tool in material science. The amount of material interaction depends on the energy, or wavelength of light and can provide a wealth of information about that material’s physical properties.
- IR Spectroscopy, Soil Analysis Applications,
- Structural and Mechanistic Enzymology
- Electronic Spectroscopy, Environmental Applications
- Rotational coherence spectroscopy
- Terahertz and far-infrared spectroscopy
- Laser spectroscopy in medical diagnostics
- Neuroimaging
- Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- Luminescence spectroscopy
Track 7: Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics is that the study and application of electronic devices and systems that supply, observe and control light. Light source is used in optoelectronics and optical fibre telecommunication for information transmission. In optical fibre interferometers, optical fibre lasers, sensors and fibre modulators. Light defines solely the electro-magnetic radiation from the visibleness of 380-780 nm, whereas in several applications. Light-detecting devices are often used for light sensing and communication. Samples of these embrace darkness-activated switches and remote controls. In normal terms, light-detecting devices work by exploitation photons to liberate bound electrons among semiconductor materials. Light-emitting devices use voltage and current to provide radiation (i.e., light). Such light-emitting devices are usually used for functions of illumination or as indicator lights. In distinction, light-detecting devices, like phototransistors are designed to convert received magnetic attraction energy into electrical phenomenon or voltage. Over a successive decade, the look of optoelectronics packaging would require vital changes to be efficient and simply factory-made.
Optoelectronic integrated circuits Photoelectric or photovoltaic effect, used in photodiodes (including solar cells), phototransistors, photomultipliers, optoisolators, and Integrated Optical Circuit (IOC) elements. The Optoelectronics market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18% from 2012 to 2020 and reach $4.21 billion in 2020.
- Optoelectronics business opportunities
- Optoelectronic devices and materials
- Semiconductor materials and applications
- MEMS and NEMS
- Optoelectronic Instrumentation, measurement and metrology
- Optical fibre sensors/detectors
- Semiconductor nanostructures for electronics and optoelectronics
- Photoelectric or photovoltaic effect
- Photodiodes (including solar cells)
- Phototransistors
- Photomultipliers
- Optoisolators
- Integrated optical circuit (IOC) elements
Track 8: Photonics
Photonics is the generation, transmission, and utilization of light and other electromagnetic radiation. Photonics offers solutions to the global challenges of our time. Photonics is considerable for future potential, Health, communication, information, mobility, energy, security, climate, sustainability.
Generated power of the Berkeley laboratory laser Accelerator 10 lakh gigawatts. The Photonics has been fancied over the last twenty years with the goal to outline the sphere of Optics, this is often created potential through the concentration of optical device power to very short pulses. Optoelectronic phenomena and its applications by one word almost like the terribly effective field of physical science.
This photonics has undistributed superposition, Dozens of data signals can be coupled into one single optical fibre and be separated again at the receiver’s end. The signals can be very finely distinguished based on their wavelength (spectral colour), polarization, and phase.
- Photonics crystals and photonic crystal fibres
- Photodetectors/ sensors and imaging
- Photonics and ultrafast electronics
- Photonics materials and devices
Track 9: Advancements in photonics
Photonics science includes the discharge, generation, variety, transmission; signal processing, strengthening, swapping, and exposure/sensing of light. It is also related to the emerging science of quantum information. In the early 1960s the term photonics developed from the first practical semiconductor, light emitters invented, and optical fibres developed in the 1970s.
Photonic atomic devices applications are developed in different fields such as precision timekeeping, metrology, navigation and Polaritonics, Polariton which is a mixture of phonons and photons will carry the fundamental information in the photonics. In the range of frequencies from 300 gigahertz to almost 10 terahertz. Most photonic applications are in the range of near-infrared light and visible. Other emergent fields include opto-atomics, in which it integrates both photonic and
- Remote Sensing and Sensors
- Diffraction and Gratings
- Fourier Optics and Signal Processing
- Power photonics and green photonics
- Display technology
Track 10: Microwave Photonic Subsystems.
Microwaves are essential for correspondences, and frameworks for recognizing microwaves are vital for space science. Microwave Photonics (MWP) involves interactions between the RF/microwave/ millimetre-wave and the optical portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Photonics is utilized for the generation, transmission, detection, processing, and control of microwave signals with direct applicability to antenna systems (e.g., wireless and array), sensing, and instrumentation. This technology also makes it possible to have functions in microwave systems that are complex or even not possible in the radio-frequency domain and also creates new opportunities for telecommunication networks.
Microwave Photonic Systems, Inc. is a high-tech full service design and integration engineering firm that specializes in the design, development and manufacture of Radio Frequency / Microwave and Fiber Optic components and systems.
- Signal Processing Subsystems for RF Photonics
- A Silicon Integrated Microwave-Photonic Transceiver
- RF photonic techniques
- Simultaneous transmit and receive (STAR)
- wideband EW receivers
Track 11: Optics in Medicine
Since ancient times, Optics being used as an aid for the examination of patients and in some beneficial treatments. Many of the optic medical instruments in use today raised to developed in the nineteenth century and, with the advent of optical fibers and laser sources in the mid-twentieth century, a new generation of medical devices, instruments, and techniques have been developed that have helped modernize medicine and perform task unimaginable only a few decades ago. This chapter illustrates—through several optical instrument and application examples—the uses, benefits, and future prospects that optics brings as an enabling technology to the medicine and the overall healthcare industry.
- Optometry
- Clinical technologies and systems
- Biomedical spectroscopy
- Artificial vision and colour
- Tissue optics
- Optical coherence tomography
- Biomedical Optics
- Optoacoustic imaging of biological tissues
Track 12: Technologies in optics and photonics
Optical technology can further the fields of medicine, science and engineering through the development and application of new technologies. The process of transmitting information from one place to another place by transferring pulses of light through an optical fibre is known as fibre optic communication. Many telecom companies use Optical fibre to forecast Internet communication, telephone signals, and cable television signals. Semiconductor lasers/laser diodes play a dynamic role in our everyday lives by providing economy and compact-size lasers. They contain complex multi-layer structures requiring elaborate design and nanometer scale accuracy.
Likewise, optical device and optical technology will more the fields of medication, science and engineering through the event and application of latest technologies. Liquid-crystal display. In an optical device and optical technologies, professionals channel these beams to be used in scientific instruments, engineering, medicine analysis, communication and medication. Lasers emit high-intensity light beams.
- Liquid-crystal display
- Light-emitting diodes
- Lasers and fibre optics
- Charge-coupled devices
- Diffractive and Holographic Optics
- Laser measurement technology
- Optical analytics
- Data processing systems
- Laser material processing
- Semiconductor technology
- Nonlinear optics
- Solid state lasers
- Solar energy
- Production measurement technology
- Image processing
Track 13: Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics is that the study and application of electronic devices and systems that supply, observe and control light. A light source is used in optoelectronics and optical fibre telecommunication for information transmission. In optical fibre interferometers, optical fibre lasers, sensors and fibre modulators. Light defines solely the electromagnetic radiation from the visibleness of 380-780 nm, whereas in several applications. Light-detecting devices are often used for light sensing and communication. Samples of these embrace darkness-activated switches and remote controls. In normal terms, light-detecting devices work by exploitation photons to liberate bound electrons among semiconductor materials. Light-emitting devices use voltage and current to provide radiation (i.e., light). Such light-emitting devices are usually used for functions of illumination or as indicator lights. In distinction, light-detecting devices, like phototransistors are designed to convert received magnetic attraction energy into electrical phenomenon or voltage. Over a successive decade, the look of optoelectronics packaging would require vital changes to be efficient and simply factory-made.
Optoelectronic integrated circuits Photoelectric or photovoltaic effect, used in: photodiodes (including solar cells), phototransistors, photomultipliers, optoisolators, and Integrated Optical Circuit (IOC) elements. The Optoelectronics market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18% from 2012 to 2020 and reach $4.21 billion in 2020.
- Optoelectronics business opportunities
- Optoelectronic devices and materials
- Semiconductor materials and applications
- MEMS and NEMS
- Optoelectronic Instrumentation, measurement and metrology
- Optical fibre sensors/detectors
- Semiconductor nanostructures for electronics and optoelectronics
- Photoelectric or photovoltaic effect
- Photodiodes (including solar cells)
- Phototransistors
- Photomultipliers
- Optoisolators
- Integrated optical circuit (IOC) elements
Track 14: Optical Telecommunications
A method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber is known as Optical telecommunication. Light makes an electromagnetic carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. High bandwidth, long distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required for the electrical cabling over a fiber optical media. In many telecommunications companies to transmit telephone signals, Internet communication, and cable television signals Optical fiber is used. At Bell Labs researchers have reached internet speeds of over 100 petabytes per second using fiber-optic communication.
Companies like AT&T, MCI, and U.S. Sprint use optical fibre cable to hold plain old telephone company (POTS) across their nationwide networks. Since its invention within the early Seventies, the utilization of and demand for optical fibre have full-grown hugely. The uses of fiber these days are quite varied. With the explosion of data traffic because of the web, electronic commerce, pc networks, multimedia, voice, data, and video, the requirement for a transmission medium with the bandwidth capabilities for handling such large amounts of data is overriding. native telephone company providers use fiber to hold this same service between office switches at additional native levels, and generally as so much as the neighbourhood or individual home. fibre is also used extensively for transmission of information signals. Fiber optics, with its relatively infinite bandwidth, has proved to be the solution.
- Semaphore line
- Semaphore signal flags
- Optical fiber
- Signal lamps
- Photophone
- Free-space optical communication
- Heliograph
Track 15: Optical sensors technologies and types
Taking advantage of the ability of optical fibers to transmit and receive optical signals over vast distances, a current trend is to form systems of sensors, or sensing element arrays. This avoids having to convert between physical science and photonics individually at every sensing places, thereby reducing prices and increasing flexibility. As indicated earlier, most sensors these days involve the utilization of fibers somewhere within the technique and are remarked as optical fiber sensors. Optical sensors create use of a similar physical phenomenon to perform their sensing operation but involve no fibre. They instead consider lens or mirror systems to transmit and manipulate the beams of light utilized in their sensing process. The fiber and optical sensors field are active slightly over a decade, with the patent record starting earlier, as can be expected, and showing growth almost like that of publications.
For the foremost part, chemical sensors are samples of remote qualitative analysis using fiber optics as a relay vehicle. each absorption and visible radiation spectroscopy are used. Chemical testing has been demonstrated exploitation fibre-optic fluoroimmunoassay (FOFIA). during this technique, antigens specific for the antibodies to be detected are immobilized in proximity to a guided optical beam. The antibodies are labelled with fluorophores and allowed to bond to the antigens. temporary excitation of the fluorophores and/or the assortment of the resulting fluorescent radiation give for terribly sensitive observance techniques. In some tests, 10 -12 molar levels of creatine kinase (CK-MB) are detected.
- Importance and role of optical fibres
- Advantages and disadvantages of Optical Sensors
- Chemical sensors
- Temperature sensors
- Promising new optical sensor technologies
- Biomedical sensors and Strain sensors
- Electrical and magnetic sensors
- Rotation sensors and Pressure sensors
- Displacement and position sensors
- Acoustic and vibration sensors
- Miscellaneous sensors
- Special fibres for sensors
- Light sources and Detectors
Track 16: Applied Industrial Optics
Optics is a branch of Physics that comprises of behaviour and characteristics of light, and relations with materials and the manufacture of tools that use or distinguish it. In general, optics defines the characteristics of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared (IR) light. As light is an electromagnetic radiation, other types of radiation like X -rays, microwaves, and radio waves display similar properties. Optics is a part of daily life. The ubiquity of visual systems in biology indicates the central role optics plays the science of one of the five senses. With advanced evolution in the optical sensors, consumer market players have offered power-efficient optical sensors. The Europe optical sensors market is expected to grow to USD 3.85 billion by 2018 at a CAGR of 5.73% over the period 2016-2021.With advanced evolution in the optical.
- LED/Laser lighting
- Optics and Energy
- Autonomous/Automated Systems
- Remote Sensing
- Non-destructive Evaluation/Non-invasive testing
- Biomimetic
- Smartphone Optics
- Wearable Technology
Track 17: Optical imaging and sensing
Optical imaging may be a technique to look at during a non-invading manner within the body, similar what's done with x-rays. But, not like x-rays, that use radiation, optical imaging uses light and therefore the special properties of photons to get elaborated images of organs and tissues yet as smaller structures together with cells and even molecules. These pictures are utilized by scientists for analysis and by clinicians for illness diagnosing and treatment. an optical device may be a device that converts light rays into electronic signals. the same as a photoresistor, it measures the physical amount of light and translates it into a form scan by the instrument. Generally, the optical sensing element is a component of a bigger system assimilating an instrument, a supply of light and therefore the sensing element itself. this can be usually connected to an electrical trigger, that reacts to a modification within the signal inside the light sensing element.3D Printed Optics and Additive Photonic Manufacturing
- Digital Optics for Immersive Displays
- Unconventional Optical Imaging
- Optical Micro- and Nanometrology
- Optics, Photonics and Digital Technologies for Imaging Applications
- Optical Sensing and Detection
- Imaging in Biology and Medicine
Track 18: Continuity of services and mobility
Internet Protocol (IP) is considered as the base element of all communications. Access technologies, such as LTE and GPON, accelerate this process. In addition, at the level of services, the IMS is also a key element which should gradually support major telecommunications services, as part of an overall development strategy of the current legacy networks, fixed and mobile, towards a NGN (Next Generation Network) architecture, providing universal services.
- Framework technologies: LTE/EPC & IMS
- Types and level of mobility execution
- Single Radio Voice Call Continuity
Track 19: Emergency communication system (ECS)
Quickly establishing a temporary communication system to support emergency management is one of the most urgent tasks in the disaster relief mission. To facilitate the rescue teams and victim people to communicate inside and outside the disaster site, this paper proposes an integrated communication system by composing heterogeneous wireless networks. Firstly, wireless sensor network (WSN) and mobile ad hoc network (MANET) are deployed on the disaster site for local communication and information collection. To communicate with the remote disaster-safe areas, satellite gateway is used for the local networks to interconnect with the satellite mobile network. Furthermore, cellular gateway is used as an alternative remote communication means when the expansion of local networks reaches a working cellular base station. The overall system architecture, the relevant network elements, and the methods of establishing and integrating them to be a mission system are described. The proposed system can help to reduce the network deployment time, support more terminal types, and provide emergency management services.
- Modes of communication
- Broadcast technologies
- Mass Notification
- Risk Analysis
- Receive emergency info
Track 20: Telecommunication Networks
While deployment of new network technologies has not been steady over the years, it is useful to take a long-term view of how major new telecommunications infrastructures evolve. A telecommunications network is a collection of terminal nodes, links are connected so as to enable telecommunication between the terminals. The transmission links connect the nodes together. Next Generation Network(NGN) is a concept for the defining and establishing of the networks, allowing a formal distribution of functionalities into separate layers and planes by using open interfaces, Since the beginning of this decade, we have witnessed the emergence of new generations of three major communication networks. The market conditions, technology innovations, and services driving the need for intelligent all-optical, 3G wireless, and QoS-based packet networks. Market forces such as traffic and subscriber growth, equipment cost reduction, and new technology penetration have a deep impact on network buildouts. Technology innovations abound, especially in the optical domain. For example, Raman amplification, pure optical switches, and tunable lasers have had a major impact on the architecture of optical networks. Many key services, such as streaming audio and high-quality image transfer, were not possible using wireless access because of its limited bandwidth and performance. With 3G wireless technology, a true mobile Internet will become a reality. Businesses have shied away from the use of the public Internet because of service quality.
- Transmission networks
- Signaling and Control
- Data (packet) Switching and Routing
- Mobile Switching systems and Network
The worldwide fiber optics market trend was valued at USD 5.39k million in 2016 and is expected to understand traction over the forecast extent. The trade presents promising growth prospects across the forecast quantity in the assessment of a combination of things exactly increasing investments and analysis undertaken by notable players at intervals the business to develop and upgrade the optical technology application arena. Optical technology has gained prominence over the past few years, as a result of persistent analysis & development activities and so the escalating demand for high metric communication and information services.
Market Analysis of Optics from 2014 to 2025 in USD (millions)
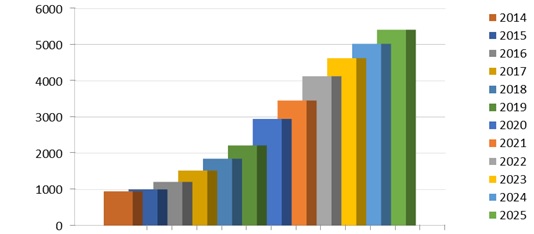
If you're a telecommunication representative at this essential juncture, you wish to create 2 completely different moves at a similar time. First, begin the task of modernizing operations. Second, redefine your strategic identity (your price proposition) for the longer term — specifically; what you'll be able to expect to supply customers 5 or ten years from currently. It may well be — perhaps it should be — that after going through this journey, your company will look very different from today’s version.
US shoppers are gazing their devices over nine billion times daily within the combination up 13 % from last year. Smartwatch penetration doubled from 2014 to 2015 and tripled in 2016; smartwatches have currently penetrated roughly 12 % of the mobile client market within the USA. However, in 2017 we have a tendency to may even see a shift toward areas with a better growth potential that goes well on the far side carriers’ core property business.
In addition, there are innovative things in store in terms of communications to appear forward to the present year as well. The telecom business itself survives by the tagline, where you go, our network follows. This sturdy and reliable network can still follow the United States through 2017 similarly. Network providers are the endeavor to form 5G a reality as shortly as potential. Telco’s around the world have already developed the 5G design and have initiated the workplace and field trials for the essential property parts within their race to achieve a competitive advantage in the market. The promise of 5G – more speed, larger potency and fewer latency- are a significant push for connected things within the future.
The IT and Telecommunications business faces substantial changes that end in intense competition and continuous want for innovation. At Infiniti, we've got a large vary of industry-leading solutions to assist purchasers to track key developments in these markets, adapt to changes and thereby guaranteeing they maintain a competitive advantage. These solutions together with our team of specialists provide a comprehensive view of the market landscape, to assist clients to create effective business decisions, in order to grow, expand, diversify, tackle competition and mitigate risks.
|
· The university of Arizona |
|
· The Institute of Optics |
|
· University of Gothenburg |
|
· University of Rochester |
|
· Clemson University |
|
· University of Oslo |
|
· University of Waterloo |
|
· Institute of Technical Optics |
|
· Pacific University |
|
· University of California |
|
· University of Pittsburgh |
|
· Oklahoma State University |
|
· University of North Carolina at Charlotte |
|
· Albright College |
|
· University of North Texas |
|
· University of New Mexico |
|
· Montana State University |
|
· Indiana University of Pennsylvania |
|
· Delaware State University |
|
· Cleveland State University |
|
· Tampere University of Technology |
|
· Purdue university |
|
· Monroe Community college |
|
· ITMO University |
|
· University of Bern |
|
· Bar Ilan University |
|
· University of Colorado Boulder |
|
· Georgia State University |
|
· University of Liverpool |
|
· Queen's University Belfast |
|
· Swansea University |
|
· University of Nottingham |
|
· University of Strathclyde |
|
· University of Strasbourg |
|
· University of Southampton |
|
· University of Auckland |
|
· Universidade do Contestado |
|
· Sofia University St. Kliment Ohridski |
|
· University of Montreal |
|
· University Foundation of the Andean Area |
|
· University San Martín Foundation |
|
· Antonio Nariño University |
|
· Universidad de La Salle |
|
· Universidad del Bosque |
|
· Universidad Metropolitana |
|
· Santo Tomás University |
|
· Czech Technical University |
|
· Masaryk University |
|
· Palacký University |
|
· Metropolitan University |
|
· University of El Salvador |
|
· Institute of Vision Sciences |
|
· Higher Institute of Optics |
|
· University Paris-Sud |
|
· Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology |
|
· University of Cape Coast |
|
· Technological Educational Institute of Athens |
|
· The Hong Kong Polytechnic University |
|
· University of Florence |
|
· University of Milano-Bicocca[38] |
|
· University of Padua, Italy [39] |
|
· University of Naples Federico II |
|
· University of Roma Tre |
|
· University of Salento[40] |
|
· University of Turin |
|
· University of Latvia |
|
· American University of Science and Technology |
|
· Lebanese University |
|
· Higher Industrial Technical Institute |
|
· Modern University for Business and Science |
|
· International Islamic University Malaysia |
|
· International University College of Technology Twintech |
|
· Management & Science University |
|
· National Institute of Ophthalmic Sciences |
|
· SEGi University College |
|
· National University of Malaysia |
|
· Universiti Teknologi MARA |
|
· National Polytechnic Institute |
|
· National Autonomous University of Mexico |
|
· Universidad Autónoma de Aguascalientes |
|
· Autonomous University of Ciudad Juárez |
|
· Xochicalco University |
|
· Tribhuwan University |
|
· University of Applied Sciences Utrecht |
|
· New Zealand National Eye Centre |
|
· Abia State University Uturu |
|
· Bayero University |
|
· Federal University of Technology Owerri |
|
· Imo State University, Owerri |
|
· Madonna University Okija |
|
· University of Benin |
|
· University of Ilorin |
|
· Buskerud University College |
|
· Cebu Doctors' University |
|
· University School Center |
|
· Davao Doctors' College |
|
· Lyceum-Northwestern University |
|
· Manila Central University |
|
· Mindanao Medical Foundation College |
|
· Southwestern University |
|
· Adam Mickiewicz University |
|
· Poznan University of Medical Sciences |
|
· University of Warsaw |
|
· WrocÅ‚aw University of Technology |
|
· University of Beira Interior |
|
· University of Minho |
|
· The Helmholtz Research Institute for Eye Diseases |
|
· Saint Petersburg Medical Technical College |
|
· King Saud University |
|
· Qassim University |
|
· Ngee Ann Polytechnic |
1) International Conference on Condensed Matter Physics , August 16-17, 2018, London, UK ;
2) International Conference and Exhibition on Lasers, Optics & Photonics, September 08-10, 2014,Philadelphia, USA
3) International Conference and Exhibition on Lasers, Optics & Photonics, September 01-03, 2015, Valencia, Spain
4) International Conference and Trade Fair on Laser Technology, July 20-22, 2015, Florida, USA
5) International Conference on Photonics, July 28-29,2016, Berlin, Germany
6) International Conference and Exhibition on Lasers, Optics & Photonics, Nov 15-17, 2017, Las Vegas, USA
7) International Conference on Photonics, July 31- August 01, 2017, Milan, UK
8) International Conference on Quantum Physics and Quantum Technology, September 25-26, 2017, Berlin, Germany
9) International Conference on Physics, June 27-29, 2016, New Orleans, USA
10) Global Optometrist Meeting and Trade Fair on Laser Technology, July 28-29, 2016, Berlin, Germany
11) International Conference on Optics, Photonics and Lasers (OPAL' 2018), 9-11 MAY 2018, BARCELONA, CASTELLDEFELS, SPAIN;
12) International Conference on Quantum Mechanics and Applications, July 20-21, 2018; Atlanta, USA;
13) International Conference on Atomic Physics, October 26-27, 2018, Boston, Massachusetts, USA;
14) International Conference on Theoretical Physics, November 27-29, 2018, Los Angeles, USA;
15) International Conference on Planetary Science and Particle Physics August 27-28, 2018 Boston, Massachusetts, USA;
16) Workshop on Graph Spectra, Combinatory and Optimization, January 25-27, 2018, University of Aveiro, Aveiro, Portugal;
17) Conference on Numerical Analysis and Scientific Computation with Applications (NASCA 2018); July 2-6, 2018; Kalamata, Greece;
18) The Conference on Electro-Optics, 5 - 10 May 2018, San Jose, CA, United States; The Conference on Electro-Optics , 13 - 18 May, 2018; San Jose, CA, United States;
19) International conferences on Optoelectronics, September 19-20, 2018, Philadelphia, USA;
20) International Conference on Theoretical Physics, July 02-03, 2018, Vienna, Austria;
21) International Conference on Plasma Physics, October 15-16, 2018, Ottawa, Canada;
22) International Conference on Astrophysics Physics, December 03-05, 2018, Chicago, Illinois, USA;
23) OSA Bio photonics Congress: Biomedical Optics, 3-6 Apr 2018, Hollywood, FL, United States, Laser Ultrasonic, July 09-13, 2018, Nottingham, United Kingdom;
Conference Highlights
- Optics
- Optical Communication and Networks
- Optoelectronics
- Semiconductor nanostructures for optoelectronics
- Quantum optics
- Photonics
- Advancements in photonics
- Microwave Photonic Subsystems.
- Optics in Medicine
- Technologies in optics and photonics
- Optical Telecommunications
- Optical sensors technologies and types
- Applied Industrial Optics
- Optical imaging and sensing
- Continuity of services and mobility
- Emergency communication system (ECS)
- Telecommunication Networks
- Special issue on optoacoustic imaging and sensing
- Spectroscopy
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 22-23, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by




























































